Ear wax naturally works its way out of the ear canal, carrying contaminants away. However, sometimes it builds up to a point where it can obstruct hearing and contribute to problems with hearing technology.
It’s important to avoid using cotton swabs to clean ears, as this can disrupt this natural process and cause damage. Audiologists can provide professional earwax removal to improve ear health.
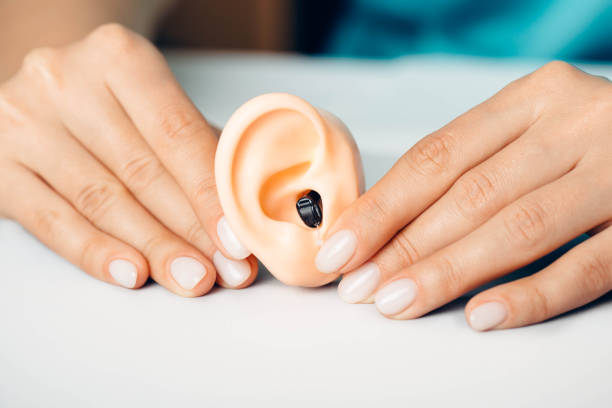
Earwax Removal
Earwax is produced by your body to protect the ear canal, which acts as a kind of conveyor belt bringing food into the ear and carrying out dead skin cells and other debris. However, excess earwax can build up and block your ears, which is why ear cleaning is important.
Removing ear wax is a quick and relatively painless procedure. However, impacted earwax can be more difficult to remove and may require professional treatment. a consultation with the Melbourne Audiology Centre is the best way to determine if earwax is a problem and recommend a method for removal.
Over-the-counter earwax cleaners such as cotton swabs should be avoided, as they often push earwax back into the ear canal and can rupture your eardrum. In addition, ear candling, which involves holding a candle in the ear canal for several minutes to uproot earwax, is not recommended, as it can cause infection and damage your eardrum.
Your audiologist may recommend ear drops, which soften the earwax and help it to drain out of the ear canal. To use the drops, lie on your side with your blocked ear up and place 5 drops in the ear canal. Then, wait for a few minutes and tilt your head to allow the fluid to drain out.
Ear Canal Cleaning
A clean ear canal can eliminate impacted earwax, restoring hearing and alleviating discomfort. Your audiologist can use specialized tools like suction devices and curettes to clean out the outer and inner ear canals, as well as offer tips for home care that can prevent future wax build-up, and they can check if it is time to wear a hearing aids bundoora or not.
Your ears naturally produce earwax, also known as cerumen, to protect your inner ears from dust and debris. Earwax is important to your health, as it helps to inhibit the growth of bacteria and keeps small particles of dust from entering your ear canals. However, some people’s glands may over-produce earwax, leading to a blockage of the ear canal and resulting in symptoms such as an earache, a full feeling in the ears, or muffled hearing.
It’s best to leave ear cleaning to ear wax removal in Melbourne, as attempting to reach into your own ear canal can cause damage. In particular, a cotton swab can push ear wax deeper into the ear canal and possibly puncture the eardrum. This can lead to a number of complications, including chronic ear infections and ear drum perforations.
Aside from avoiding cotton swabs, you can also help to avoid earwax build-up by wearing soft earplugs during loud events and using a humidifier at night to keep the air moist in your ear canal. Additionally, over-the-counter earwax removal solutions and sprays can be safe if used as directed.
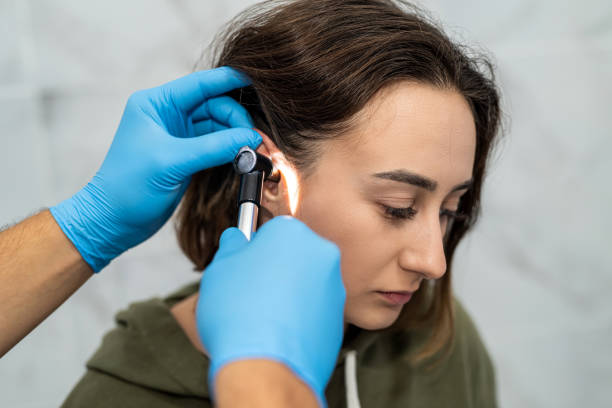
Ear Infection Treatment
Most people overlook their ears, but your hearing is incredibly important. This makes it essential to give your ears the attention they deserve, which includes routine care and prevention of ear infections.
An ear infection occurs when bacteria or viruses invade the small space behind the eardrum. This area houses three tiny bones that help you hear and is connected to the back of your nose and throat through a passageway called the eustachian tube. When the eustachian tube is blocked, as with a cold or allergies, fluid builds up in the middle ear creating an environment perfect for infection. This is a type of otitis media (OM) and it usually affects children.
During otitis media, you may notice symptoms like an earache or your ear feeling full. Your health care provider will diagnose the condition with an otoscope, which shines a light into your ear canal and eardrum. She will also use a tool called tympanometry to check for fluid in the middle ear and obstruction in your ear canal.
Your healthcare provider will likely prescribe eardrops and/or antibiotics to treat the infection. She might also recommend autoinsufflation, in which you pinch your nose and exhale to adjust air pressure in the ear. In severe cases, your doctor might have to place a small tube in your ear. This helps prevent fluid from building up and improves your ability to hear, but these tubes usually fall out on their own after 6 months to a year.
Tinnitus Treatment
Constant noise in your head—called tinnitus—rarely indicates an underlying medical condition, but it can certainly be annoying. Tinnitus can sound like ringing in the ears, whistling, buzzing, hissing, chirping, or roaring and may come and go. It can also be in one or both ears and constant or pulsating.
Most tinnitus is subjective, meaning you alone can hear it. However, some people experience a whooshing sound that matches their heartbeat (pulsatile tinnitus). This form of tinnitus is usually audible to your doctor with a simple stethoscope and can indicate vascular problems.
To determine the cause of your tinnitus, your doctor will do a physical exam, including a careful examination of your ears. He or she will ask you about your history and symptoms, check for medications that can affect hearing and tinnitus, and perform a general audiological test to assess your hearing. Depending on your symptoms, imaging techniques such as an MRI or CT scan may be required.
If a cause for your tinnitus is identified, treatment can often eliminate it or significantly reduce its intensity. In some cases, a psychologist or counselor may help with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). CBT uses techniques such as self-reflection and relaxation to change the way you think about your tinnitus and its impact on your life. The therapy is usually short-term, involving weekly sessions for two to six months.