The human foot is an evolutionary marvel with 26 bones, 33 joints and more than 100 muscles, ligaments and tendons that work together to get you from one place to another. Preventing serious foot problems starts with inspecting your feet on a regular basis and taking action when you notice any changes.
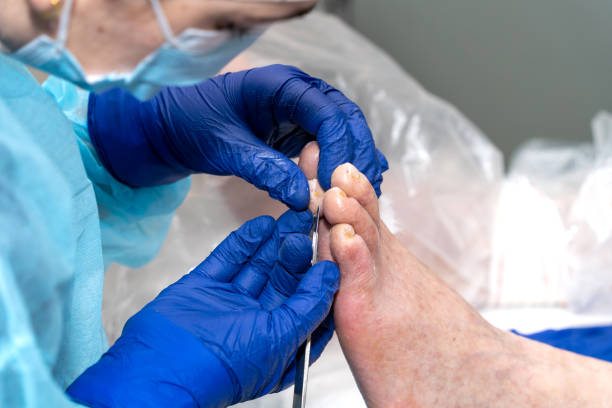
Bunions
A bunion is a painful, bony bump that forms on the inside of your foot at the base of your big toe. It develops gradually over time as the bones in your feet shift, causing certain ligaments to stretch and others to tighten. This condition is more common in women and may be related to the way they wear shoes that put pressure on their toes.
Bunion symptoms can be eased by over-the-counter bunion pads and splints that keep your big toe in a normal position. Wearing well-fitting shoes with wide toe boxes and performing regular foot exercises such as toe stretches and foot rolling can also prevent bunions from getting worse and promote healthy feet.
Neuromas
Your feet support your body weight, and take a beating every day. They’re also the first place that some health problems show up, like joint stiffness or swelling.
If you feel like you are walking on marbles in the ball of your foot (the forefoot), you may have a Morton’s neuroma, which is a thickening of tissue around a nerve that leads to your toes. This condition usually develops in middle-aged people, and is caused by irritation or compression of the nerve. Over-the-counter ibuprofen can help reduce pain and swelling. In some cases, decompression surgery is needed, which involves cutting nearby structures to relieve pressure on the nerve and provide relief.
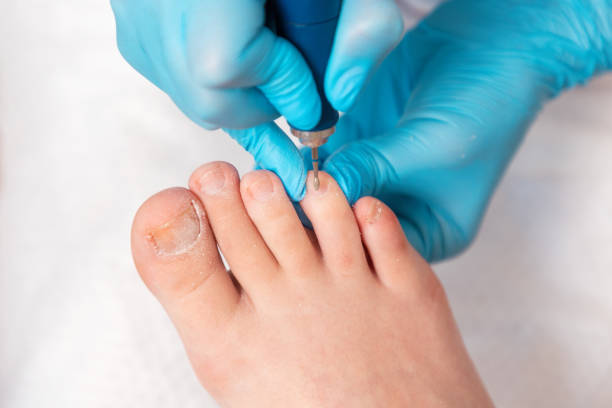
Ingrown Toenails
Ingrown toenails occur when the edge of the nail pierces or cuts the skin around it. Over time this can lead to infection. Home treatment includes soaking the foot in warm water with Epsom salt 3-4 times per day and placing bits of cotton or dental floss between the toe and the nail. Over the counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help with the pain.
Keeping nails cut straight across, and not into corners or sides, will reduce the risk of ingrown toenails. Avoid tight shoes, and alternate footwear throughout the day. If at-home treatment does not relieve the symptoms of an ingrown toenail, seek medical care from a podiatrist in Caloundra.
Plantar Fasciitis
The plantar fascia is a band of fibrous tissue that connects your heel to the ball of your foot and to your toes. It provides both static support for the longitudinal arch and dynamic shock absorption as you walk or exercise.
Patients with plantar fasciitis experience a sharp, stabbing pain in the bottom of their heel or arch when they take their first steps after waking up or after prolonged periods of standing. This pain usually lessens or goes away with continued activity, but can return later in the day.
Doctors diagnose plantar fasciitis with a physical exam and by asking patients about their symptoms. They will also recommend a variety of simple treatment methods. These include:
Achilles Tendinitis
The Achilles (uh-KILL-eez) tendon is the band of tough tissue that connects calf muscles in the back of your lower leg to your heel bone. It is used when you walk, run and jump.
Pain, stiffness and swelling in the back of your leg and especially above your heel are signs of Achilles tendinitis. It often starts as a mild ache after exercise, stair climbing or running.
Nonsurgical treatment includes over-the-counter pain medications, ice, splints to hold your foot raised during the day and at night, and physical therapy exercises. If home treatments don’t relieve your symptoms, your doctor may recommend surgery to repair the tendon. The surgery is done through a small incision in the back of your heel.
Diabetic Neuropathy
With 26 bones, 33 joints and more than 100 muscles, ligaments and tendons made of strong fibrous tissues, our feet perform an amazing feat every day. They carry us and our weight, and endure more stress than any other part of the body.
Diabetes can cause nerve damage that causes foot problems such as numbness and pain. Keeping blood glucose levels in their target range and proper foot care are essential to managing these symptoms.
People with diabetes should check their feet daily for cuts, blisters and other injuries. They should also wear well-fitting shoes and eat a healthy diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains and nuts.
Growing Feet
Children often experience foot and leg pain and are told that it is “growing pains”. Growing pains occur on the outside border of the feet at the point of a bony bump called the styloid process. They may be aggravated by running and jumping sports and narrow shoes.
Symptoms include pain and swelling, tight calf muscles, and limited range of motion when flexing the foot. Podiatry Sunshine Coast can help with over-the-counter pain medication, heel pads or shoe inserts, and calf muscle stretching exercises. In severe cases, surgery can be recommended.
Flat Feet
Flat feet occur when the arch that normally forms in your foot does not develop. This condition can cause pain, and it can also make walking or standing difficult.
The normal arch in your foot develops during infancy and childhood as a result of normal muscle, tendon, and ligament growth. However, some children have flat feet. This condition is usually harmless and does not require treatment.
Your podiatrist can suggest ways to reduce the pain of flat feet, such as wearing padded shoes and modifying activities that lead to foot pain. They may also advise you on stretching exercises and provide orthotics. Your doctor can also prescribe medications to help relieve pain or swelling.